Electric charge, symbolized as “q” or “Q”, is a fundamental property of particles that interact through electric forces. It is defined as the product of electric current “I” and the time “t” it flows, expressed as Q=It. The unit of measurement for electric charge is the coulomb (C), and it is typically measured using an electrometer.
TYPES OF ELECTRIC CHARGE
There are two types of electric charge: positive and negative.
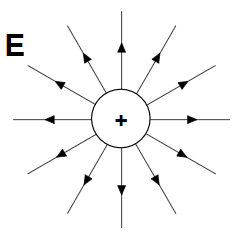
POSITIVE CHARGE
Conventionally, the charge acquired by a glass rod when rubbed with silk. Electric field lines are going away from positive charge similar as magnetic field lines from north pole of magnet.
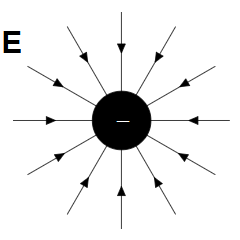
NEGATIVE CHARGE
Conventionally, the charge produced on a resin rod when rubbed. Electric field lines are going towards negative charge similar as magnetic field lines are going to south pole of magnet.
ELECTRICALLY NEUTRAL ATOMS
Atoms are electrically neutral, and most substances on Earth are also electrically neutral. For example, carbon (C) consist of 6 protons (positive charge) and 6 electrons (negative charge) which is why it is neutral.
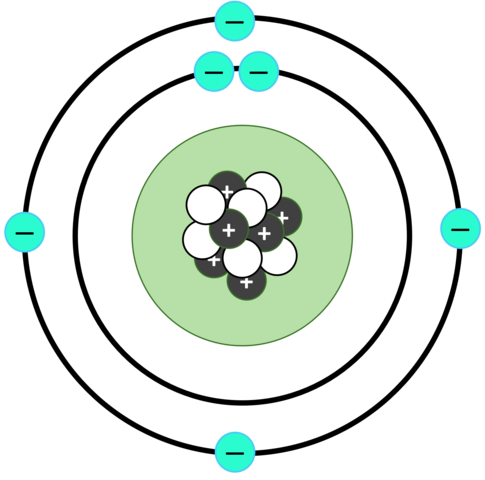
Substances become electrically charged when differently charged particles are separated, for instance, when electrons are removed from atoms.
CARRIERS OF ELECTRIC CHARGE
Negative Charge Carriers:
Usually electrons and negative ions (anions, atoms with excess electrons).
Positive Charge Carriers:
Typically positive ions (cations, atoms lacking one or more electrons), or on a subatomic level, protons.
Electric charges of bodies are always multiples of the elementary charge of an electron:
INTERACTION OF ELECTRIC CHARGES
Charged particles create an electric field around them, which is represented by electric field lines. For better understanding, it is good to check the article on magnets and magnetic fields because magnets also have similar repelling and attracting forces, and the magnetic field lines around them are similar to the electric field lines around charged particles.
Particles or bodies with equal charges repel each other:
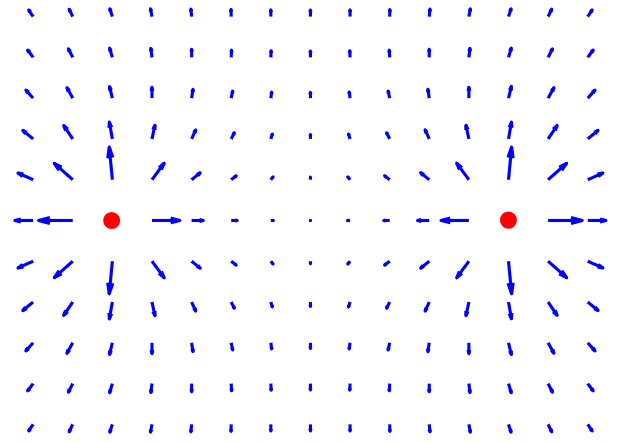
Particles or bodies with opposite charges attract each other:
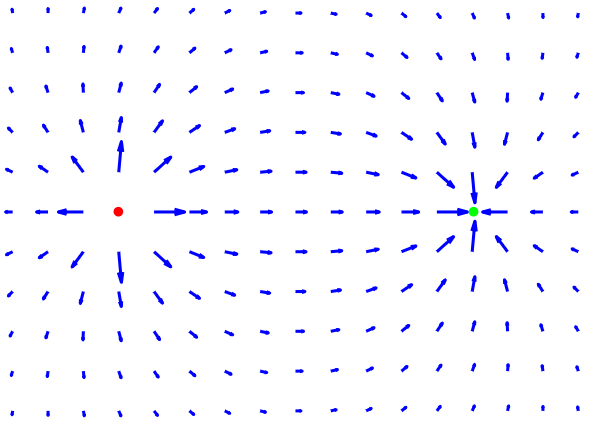
On image below red negative particle and blue positive particles atract each other while two positive particles at the same time repel each other:

Stationary electrically charged particles create electric fields, while moving charged particles generate electric, electromagnetic, and magnetic fields.


Leave a Reply to tlovertonet Cancel reply